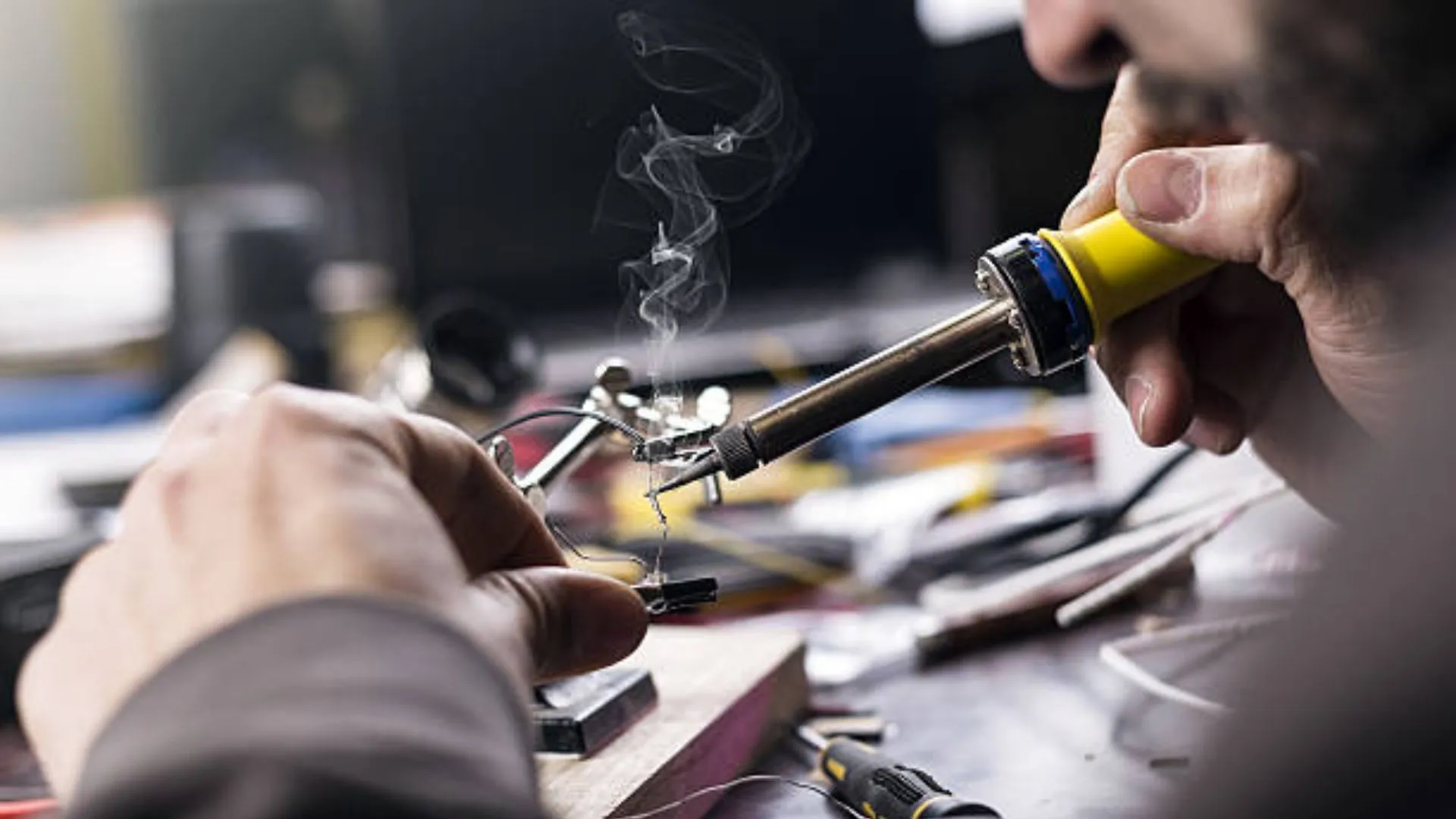
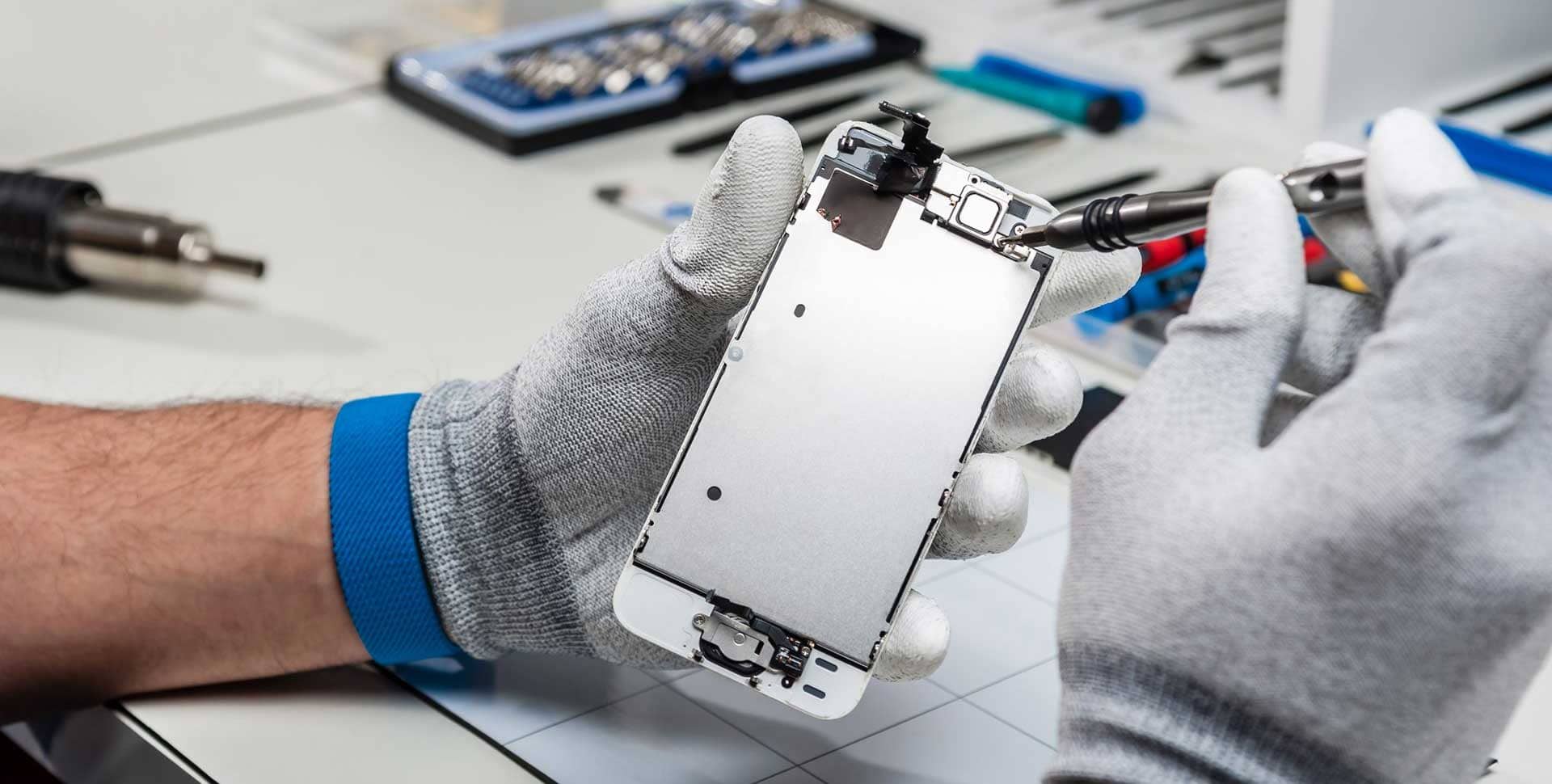
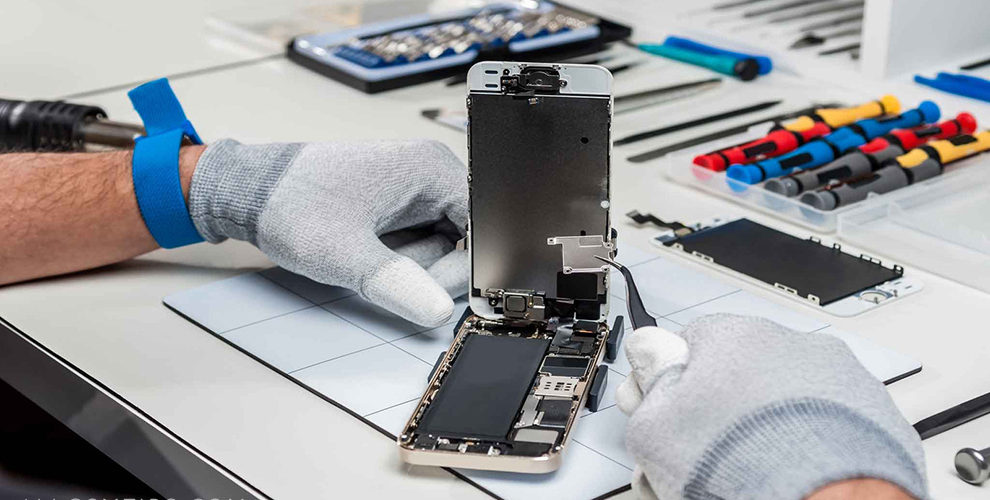
A soldering iron is one of the most important tools in cell phone repair. Whether you work on Android devices, iPhones, or basic mobile phones, soldering helps restore broken connections on the PCB. Many phone problems exist not because a component is dead, but because its solder joints have weakened, cracked, or completely disconnected.
Modern smartphones use compact motherboards. Components are tiny. Tracks are thin. One careless move can damage the board permanently. That is why soldering is considered both a basic requirement and an advanced skill in mobile phone repairing.
“Good soldering is invisible. Bad soldering is easy to spot.”
This guide explains how to use a soldering iron correctly for cell phone repair, covering tools, preparation, techniques, mistakes, and real technician-level insights. It is written for beginners as well as experienced repair technicians.
Introduction: Why Soldering Matters in Phone Repair
A soldering iron is used to join metal parts using solder wire. In mobile phones, it is mainly used on the green-colored PCB (Printed Circuit Board) to attach spare parts or repair broken electrical connections.
In repair shops, it is also commonly called:
- A soldering station
- A soldering pen
- A micro soldering iron (for fine work)
Most technicians today use a temperature-controlled soldering station because it provides stable heat and reduces board damage.
Why Phone Components Need Resoldering
Over time, solder joints inside a smartphone can fail. Common reasons include:
- Physical shock or phone drop
- Loose charging cable usage
- Excessive heat
- Repeated plugging and unplugging
- Manufacturing stress points
When solder joints fail, the component may still work but loses contact with the PCB.
Common parts that often require soldering include:
- Charging port
- Battery connector
- Power button
- Volume keys
- Headset connector
- Antenna contact points
- LCD connector (in selected models)
- Microphone or speaker terminals
In many low-cost or Chinese mobile phones, almost all components are soldered, including mic, speaker, and ringer. This reduces manufacturing cost but increases repair difficulty.
Soldering Skill: Training vs Practice
Soldering is not something you master overnight. Watching videos helps, but practice matters more than theory.
Many self-taught technicians learned soldering by:
- Practicing on dead phones
- Removing and resoldering old components
- Experimenting with different temperatures and tips
Mobile phone soldering is more delicate than soldering computer motherboards or laptop boards. The margin for error is small.
“The difference between a repair and a board replacement is often just soldering skill.”
Types of Soldering Tools Used in Phone Repair
1. Soldering Iron / Soldering Station
Used for:
- Connector soldering
- Jumper wire work
- Small component repair
Temperature control is essential for smartphone boards.
2. Micro Soldering Iron
Used for:
- IC legs
- Tiny pads
- Precision rework
3. Soldering Pen
Lightweight tool, suitable for beginners but limited in advanced work.
4. Hot Air Rework Station
Used for:
- IC removal
- BGA chips
- Shield removal
This article focuses mainly on the soldering iron, but advanced technicians often use both tools together.
Choosing the Right Soldering Iron for Mobile Repair
A good soldering setup should include:
- Temperature control
- ESD-safe design
- Interchangeable fine tips
- Stable heating element
Avoid cheap non-regulated irons. They overheat pads and damage PCBs.
Recommended temperature range for phone repair:
- Lead solder: 320–350°C
- Lead-free solder: 350–380°C
Always start lower and increase gradually.
Importance of ESD Safety in Smartphone Repair
Modern smartphones are sensitive to static electricity. A small discharge can damage ICs silently.
Basic ESD precautions include:
- ESD-safe soldering iron
- Grounded work surface
- Anti-static wrist strap
- Avoid synthetic clothing
Ignoring ESD protection is one of the biggest hidden causes of repair failure.
Role of Soldering Flux in Phone Repairs
Soldering flux is not optional. It is essential.
Flux:
- Improves solder flow
- Prevents oxidation
- Reduces heat damage
- Creates stronger joints
Always use quality flux, especially for micro soldering. Avoid acidic or low-grade flux that leaves corrosive residue.
Step-by-Step: How to Use a Soldering Iron for Cell Phone Repair
Step 1: Prepare the PCB Surface
Before soldering:
- Clean the solder points using the iron tip
- Remove old solder if required
- Make the pads flat and shiny
Dirty pads cause weak joints.
Step 2: Heat the Soldering Iron Properly
- Switch on the soldering station
- Allow it to heat for around 2 minutes
- Confirm stable temperature before starting
Never solder with a half-heated iron.
Step 3: Hold the Component Correctly
- Right-handed technicians usually hold:
- Component with left hand
- Iron with right hand
- Use precision tweezers for small parts
Never hold components directly with fingers near heat.
Step 4: Apply Solder Wire Correctly
- Take a small amount of solder wire
- Touch it to the iron tip
- Position the component on the PCB
- Touch the joint briefly
Less solder is always better than excess solder.
Step 5: Allow the Joint to Cool Naturally
- Remove the iron tip
- Do not move the component
- Let the joint cool for a few seconds
- Check strength manually
If it looks dull or weak, resolder it.
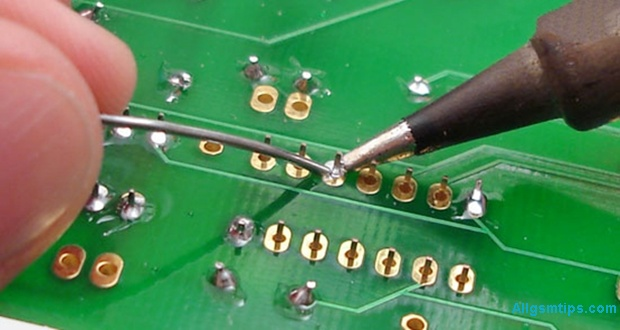
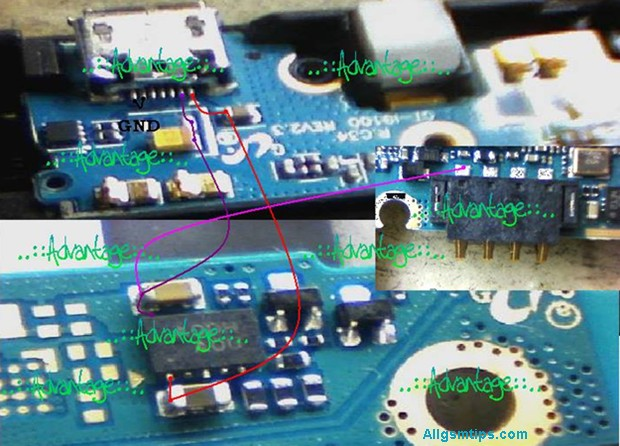
Making Jumpers Using a Soldering Iron
Jumpers are used when PCB tracks are broken. This is advanced-level repair.
Jumpers are usually made using:
- Thin copper wire
- Enamel-coated jumper wire
Only attempt jumper work if you understand circuit paths. Otherwise, you may cause short circuits.
If you do not repair motherboards at circuit level, you do not need jumper skills.
Common Soldering Mistakes Technicians Make
Avoid these common errors:
- Overheating PCB pads
- Using excessive solder
- Not using flux
- Dragging pads accidentally
- Solder bridges between pins
- Using blunt or dirty tips
Most motherboard damage happens due to impatience, not lack of tools.
Beginner Tips to Improve Soldering Skills Faster
- Practice on dead smartphones
- Start with charging ports
- Use magnification
- Clean tips frequently
- Maintain steady hand posture
Consistency improves accuracy.
Advanced Technician Tips
For experienced repair professionals:
- Use different tips for different jobs
- Combine hot air and iron strategically
- Preheat boards for complex work
- Inspect joints under microscope
- Clean flux residue after repair
Professional repair is about control, not speed.
Soldering Iron vs Hot Air: When to Use What
| Task | Best Tool |
|---|---|
| Charging port | Soldering iron |
| Button flex | Soldering iron |
| IC removal | Hot air |
| Shield removal | Hot air |
| Jumper wire | Soldering iron |
Knowing the right tool saves boards.
Safety Tips While Soldering Mobile Phones
- Never touch hot tip
- Work in ventilated area
- Avoid inhaling fumes
- Keep tools organized
- Switch off iron after use
Safety habits protect both technician and device.
Is Soldering Still Relevant in Modern Smartphones?
Yes. Despite increasing modular designs, soldering remains essential for:
- Charging issues
- Power failures
- Network problems
- Audio faults
- Board-level repair
Technicians who master soldering earn more and solve deeper issues.
“Replacing parts is easy. Repairing boards builds real skill.”
Who Should Learn Soldering in Mobile Repair?
- Beginners entering phone repair
- Advanced technicians upgrading skills
- DIY enthusiasts
- Electronics students
- Service center professionals
Soldering knowledge expands your repair capability significantly.
Final Thoughts
Using a soldering iron for cell phone repair is both an art and a technical skill. It demands patience, practice, and respect for the device. With the right tools, correct technique, and steady improvement, you can handle everything from simple connector repairs to advanced motherboard work.
Start small. Practice often. Focus on quality, not speed.
A well-made solder joint can bring a dead smartphone back to life.