A water-damaged phone can feel like a disaster. Whether your smartphone slips into the sink, gets caught in rain, falls in the toilet, or gets splashed during your day, water can easily reach sensitive components and cause serious damage. Modern smartphones—including Android devices, iPhones, and even premium waterproof models—are not fully protected from liquid exposure. Water can still enter speakers, charging ports, microphones, buttons, and even the motherboard.
But here’s the good news: Water damage does not always mean your phone is dead.
If you act quickly and follow the right steps, you can reduce the damage and improve the chances of saving your device.
“Acting fast is the difference between a temporary issue and a dead device.”
This guide offers a simple, step-by-step process based on real repair experience, updated knowledge, and practical insights from technicians who regularly handle water-damaged smartphones.
The goal is to help you avoid common mistakes, protect your data, and understand when professional help is necessary.
Understanding Water Damage in Smartphones
A smartphone contains delicate circuits and micro-components. When liquid enters the phone, it can:
- Short-circuit electrical paths
- Corrode metal components
- Damage the battery
- Affect the screen and touch response
- Block the speaker and microphone
- Interrupt charging
- Damage the logic board of the device
Even a small amount of moisture can cause long-term damage if not handled properly.
That is why the first few minutes matter the most.
Before we begin, let’s clear a popular myth:
❌ Myth: “A water-resistant phone is safe in water.”
✔ Truth: Water-resistant does NOT mean waterproof.
Water-resistance ratings (IP67, IP68) help only in controlled conditions—clean, still water, shallow depth, limited time. Real-world scenarios are different:
- Soap water
- Pool water
- Saltwater
- Hot water
- High pressure
All of these can breach seals easily.
Immediate Steps to Take When Your Phone Gets Wet
Here are the steps you must follow the moment your smartphone gets water exposure.
1. Remove the Phone from Water Immediately
The longer the device stays in water, the deeper the moisture travels.
Quick action increases the chance of saving your smartphone.
2. Turn Off the Phone Immediately
This is the most important step.
Do NOT press any other buttons.
Do NOT check whether the phone is working.
Why?
Electricity + Water = Short circuit.
Keeping the phone ON forces current into wet components, causing permanent damage.
If your mobile phone is already OFF, leave it OFF.
3. Remove the Case, SIM Card, Memory Card, and Accessories
Take out:
- Phone case
- SIM tray
- MicroSD card
- Headphones or USB accessories
This allows airflow and prevents components from trapping moisture.
4. Dry the Phone Exterior Gently
Use a soft, absorbent cloth or tissue.
Avoid:
- Shaking the phone
- Blowing forcefully into ports
- Using compressed air
These actions push water deeper into the device.
Pat dry gently instead.
5. Keep the Phone Upright to Prevent Water Spread
If liquid has entered the charging port or speaker, let gravity help.
Place the phone vertically so the water drains downward.
6. Do NOT Use Hair Dryers or Heat Guns
Excess heat is dangerous for your device.
It can:
- Warp components
- Damage the battery
- Melt adhesives
- Push moisture inside
Some people also place phones under direct sunlight. Avoid this too.
7. Do NOT Put the Smartphone in Rice
The “rice method” is one of the biggest myths.
Why you should avoid rice:
- It does NOT remove moisture inside the phone
- Rice dust can enter internal components
- It delays proper treatment
- It gives false hope
Instead of using rice, allow the phone to dry naturally or seek professional help.
What You SHOULD Do Instead: Safe Drying Methods
If you want the best chance of recovery, follow these safe, technician-approved drying techniques.
8. Use Silica Gel Packs (Highly Recommended)
Silica gel packets absorb moisture much more effectively than rice.
You can find them in:
- Shoeboxes
- Electronics packaging
- Medicine bottles
Place your device in an airtight box with silica gel for 24–48 hours.
9. Let the Phone Air-Dry Naturally
Place the phone:
- In a cool, dry place
- With good airflow
- Away from heat sources
Air drying gives moisture time to evaporate safely.
10. Do Not Charge the Phone Until Fully Dry
Charging a wet smartphone is extremely dangerous.
NEVER plug in your phone after water exposure.
Moisture in the charging port can:
- Short the charging IC
- Damage the motherboard
- Burn internal components
- Cause sparks
Wait for at least 24–48 hours before testing the device.
When to Turn the Phone Back On
After the drying period (usually 1–2 days), turn the phone ON only when:
- No visible moisture remains
- Charging port is fully dry
- Buttons respond normally
- Phone feels dry to the touch
If the device still has moisture or fog under the screen, do NOT turn it on.
Signs Your Smartphone Still Has Water Inside
Watch for these symptoms:
- Foggy camera lens
- Muffled speaker sound
- Charging error messages
- Screen flickering
- Random touch inputs
- Microphone not working
- Device heating without use
If you see any of these, do not continue using the phone. Switch it OFF and seek professional help.
You can also read How To Repair Your Cell Phone Yourself (DIY) – Easy Guide
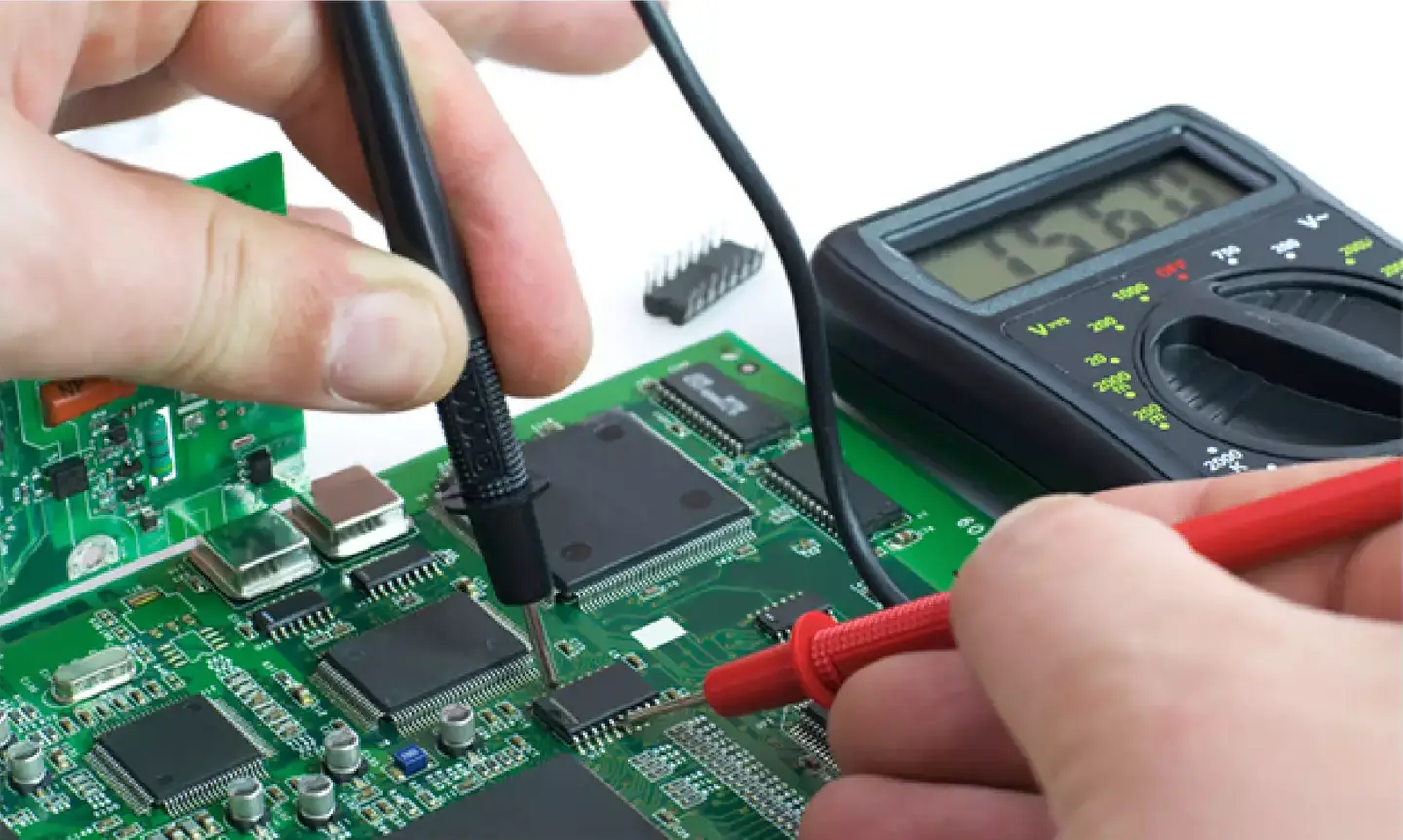
Professional Water Damage Repair Process (What Technicians Do)
If the phone does not turn on or shows problems after drying, take it to a mobile repair technician.
Water damage repair involves:
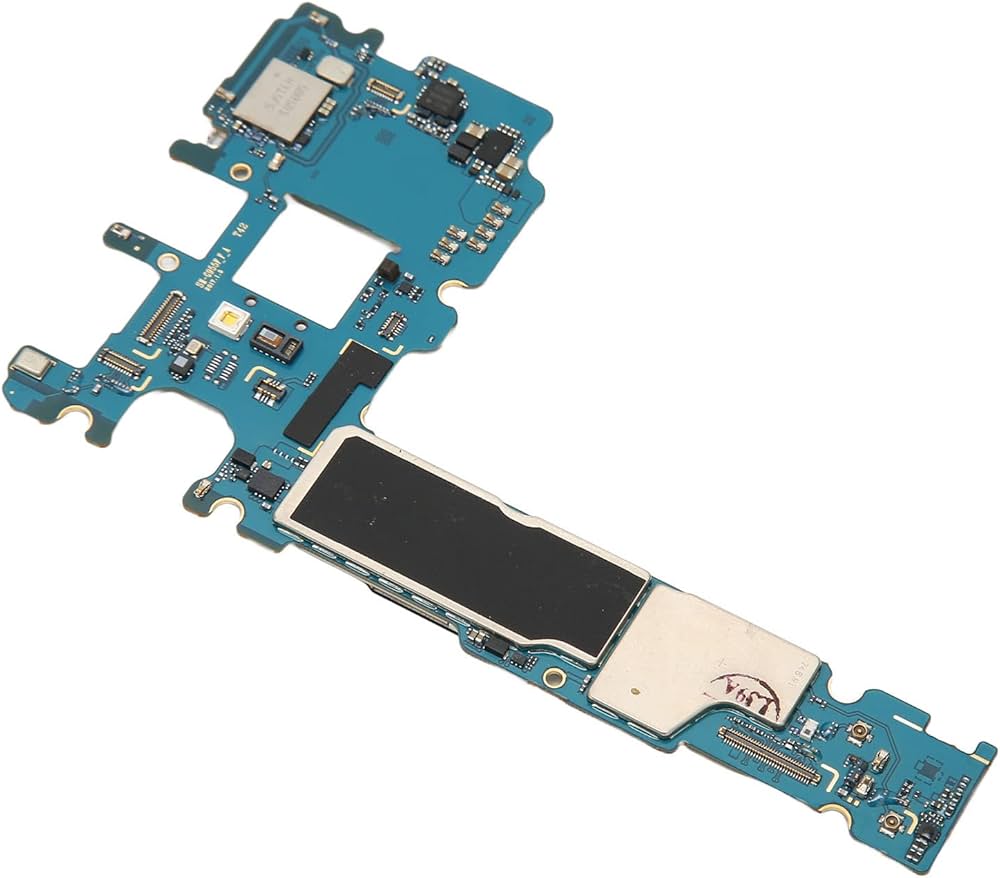
11. Disassembling the Phone
The technician opens the device to inspect the:
- Battery
- Motherboard
- Connectors
- Display interface
- Charging port
This allows accurate diagnosis.
12. Cleaning the Logic Board with Ultrasonic Machines
Professional repair shops use ultrasonic cleaners to remove corrosion, salt, and minerals from the circuit board.
This process uses:
- High-frequency sound waves
- Specialized cleaning solutions
- Controlled temperature
It safely restores many water-damaged devices.
13. Removing Corrosion and Deposits
Water leaves minerals that damage circuits.
Technicians clean these using:
- IPA (isopropyl alcohol)
- Soft brushes
- Micro tools
Removing corrosion prevents long-term failure.
14. Testing Components After Cleaning
The technician checks:
- Battery health
- Charging IC
- Power IC
- Audio IC
- Display
- Touch
- Network antennas
- Microphone and speaker
Water damage often affects multiple components.
15. Replacing Faulty Parts
If needed, the technician may replace:
- Battery
- Screen
- Charging port
- Buttons
- Camera module
- Microphone
- Motherboard components
Sometimes the entire logic board may need replacement.
Common Problems After Water Damage
Even if the device turns on, water exposure can cause long-term issues:
- Battery draining fast
- Weak charging
- Touchscreen issues
- Camera fog
- Speaker distortion
- Microphone failure
- Poor network signals
It’s important to get a full diagnosis if symptoms appear later.
How to Prevent Water Damage in the Future
Follow these simple habits to protect your smartphone:
- Use a water-resistant case
- Avoid using the phone near sinks or pools
- Keep the phone away from steam and humidity
- Dry hands before using the device
- Prevent rain exposure
- Avoid placing the device in your back pocket
- Use waterproof pouches when traveling
Prevention is always cheaper than repair.
What You Should NEVER Do With a Wet Phone
To avoid further damage:
❌ Do not turn the phone ON
❌ Do not charge the phone
❌ Do not press buttons
❌ Do not blow into ports
❌ Do not shake the device
❌ Do not use heat or dryers
❌ Do not use rice
These actions push water deeper into the device or cause short circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions About Water Damage
1. Can a completely dead water-damaged phone be repaired?
Yes, depending on the level of internal damage. Many phones recover after ultrasonic cleaning.
2. Can saltwater damage be repaired?
Saltwater causes quicker corrosion. Immediate cleaning is essential.
3. How long should I keep my phone turned off?
At least 24–48 hours before testing.
4. Will waterproof phones survive water exposure?
They resist water temporarily, not permanently. They can still get damaged.
5. Does water damage void warranty?
Yes, most manufacturers do not cover water damage.
Conclusion
A water-damaged phone does not always mean the end of your device. With the right steps—turning it off, drying it safely, and avoiding common mistakes—you can save your device or reduce the repair cost significantly. Acting quickly makes all the difference.
If your smartphone still shows issues after drying, seek professional repair.
Technicians have the tools and skills to restore components that home methods cannot fix.
“Your speed and your decisions decide whether your phone survives water damage.”
By following the safe procedures in this guide, you’ll protect your device, your data, and your investment.